The Integration of Tech In Ground Handling Services
17 February 2025
| By Just Aviation TeamGeneral aviation operations rely heavily on precision, efficiency, and adaptability. The integration of modern technology into ground handling and flight planning has revolutionized these domains, enhancing turnaround times, resource allocation, and decision-making. This guide provides an in-depth analysis of how technology is applied into the flight operations.
Benefits of Integrated Tech Systems In Ground Handling
By adopting data integration and systems interoperability, ground handling operators can transform operational efficiency while ensuring smooth coordination across diverse services. This approach not only meets the growing demands of the aviation industry but also delivers a better experience for operators and passengers alike:
- Reduced Operational Delays: Real-time communication between systems minimizes response times to schedule changes or disruptions.
- Improved Accuracy and Efficiency: Automated data exchange eliminates manual errors, particularly in high-pressure environments like turnarounds or peak traffic periods.
- Enhanced Resource Utilization: Optimized resource allocation ensures that personnel and equipment are deployed where they are needed most.
1. Real-Time Aircraft Turnaround Coordination
Ground handling involves multiple simultaneous processes, such as marshaling, refueling, and passenger transfers. Technology ensures these processes operate seamlessly.
- A live operations dashboard synchronizes aircraft arrival data from ADS-B and ATC systems.
- Upon an inbound Embraer Praetor 600, the system assigns specific ramp agents to GPU setup, lavatory servicing, and baggage unloading based on their availability and proximity.
- A time-stamped sequence ensures no delays between tasks, reducing the turnaround time from 45 to 30 minutes.
2. Predictive Maintenance for Ground Support Equipment (GSE)
Unplanned equipment failures can disrupt ground handling. IoT sensors installed in GSE enable predictive maintenance.
- A tug used for towing a Falcon 900 automatically sends diagnostic data to the maintenance team, reporting early signs of hydraulic wear. Scheduled servicing prevents unexpected downtime, ensuring the tug is operational for the aircraft’s next repositioning request.
3. Electronic Ramp Permits and Safety Logs
Paper-based logs are increasingly replaced with electronic systems to manage ramp safety and compliance in real-time.
At an airport hosting transient Learjet 45 operations, ramp agents use tablets to:
- Confirm that fueling safety zones are clear of unauthorized personnel.
- Log safety checks digitally, ensuring records are immediately available for audits and compliance reviews.
4. High-Accuracy Fuel Management Systems
Fueling operations demand precision to ensure efficiency and compliance with weight-and-balance requirements.
For a Bombardier Global 7500 requiring a specific fuel load for a transcontinental flight:
- Smart fuel dispensers connected to flight planning software with artificial intelligence (AI) calculate the exact fuel requirement, including reserves.
- Digital sensors track fuel dispensed in real time, sending live data to both the operator and the FBO.
5. Automation and Robotics
Automation has revolutionized ground handling services by integrating precision-driven systems that reduce human error and increase operational efficiency. Autonomous vehicles, leveraging advanced sensor arrays, GPS technology, and machine learning algorithms, are now pivotal in transporting baggage, cargo, and ground support equipment (GSE) across complex airport environments. These robotic systems enhance decision-making by analyzing real-time data and dynamically adjusting operations to meet on-ground demands.
Pre-Dispatch Coordination
- When a Gulfstream G500 lands, its flight data triggers an automated baggage-handling request in the airport’s integrated system.
- The system identifies the specific gate and dispatches an autonomous baggage cart from the storage area nearest to the arrival gate.
Dynamic Navigation and Safety
- Equipped with LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensors and cameras, the cart scans its surroundings to detect obstacles like refueling trucks, parked vehicles, or ramp agents.
- The cart calculates the fastest and safest route using GPS waypoints and communicates with other autonomous vehicles to avoid collisions or bottlenecks.
Adaptive Rerouting
- If an area becomes congested due to a parked fuel truck servicing a nearby Embraer Legacy 500, the cart recalculates its route.
- Using machine learning algorithms, the cart prioritizes alternate paths with minimal traffic while maintaining optimal delivery times.
Real-Time Data Sharing
- As the cart approaches the aircraft, it sends alerts to the ramp team about its arrival. This allows handlers to align operations like baggage loading or unloading without delays.
- RFID-tagged baggage loaded onto the cart ensures the correct luggage is transported, reducing mishandling risks.
6. Green Solutions in Ground Handling Operations
Transitioning from diesel-powered ground support equipment (GSE) to electric or hybrid alternatives and implementing carbon management software are pivotal steps. These solutions align with operational efficiency goals while addressing regulatory requirements for reduced carbon footprints.
Transitioning to Electric and Hybrid Ground Support Equipment
Modern ground handling services increasingly employ electric or hybrid GSE to minimize greenhouse gas emissions and operational costs.
Electric Ground Power Units (GPUs)
Electric GPUs provide a sustainable alternative to auxiliary power units (APUs), which burn jet fuel during aircraft turnarounds. Operational Workflow;
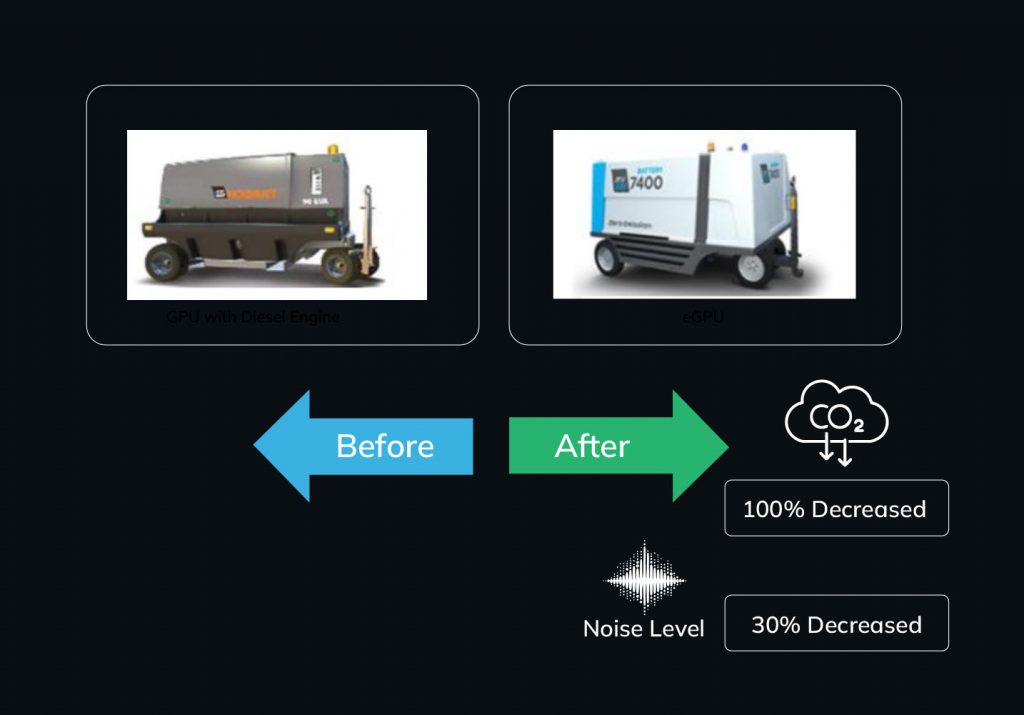
Deployment
- For a Gulfstream G650 during a 90-minute turnaround, the electric GPU connects to the aircraft immediately after engine shutdown, delivering power for cabin lighting, air conditioning, and avionics systems.
- This eliminates the need for the APU, which would otherwise consume approximately 200 liters of jet fuel, emitting over 500 kilograms of CO₂.
Monitoring and Optimization
- The GPU’s integrated energy management software monitors power usage in real time, ensuring optimal performance and avoiding energy wastage.
- A central system records GPU activity, providing data for both operational analysis and carbon footprint tracking.
Scalability
- During peak hours at a busy FBO, multiple electric GPUs are scheduled and assigned automatically based on arrival and departure slots, ensuring efficient resource utilization.
Additional Benefits
- Reduced noise pollution compared to traditional APUs, enhancing the working environment for ground staff and nearby personnel.
- Decreased maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts in electric systems.
Electric Baggage Tractors
Electric baggage tractors offer a cleaner, quieter alternative for towing baggage carts, supporting sustainability without sacrificing performance. Operational Workflow;
Charging and Readiness
- Electric tractors are charged during off-peak hours using smart charging stations that prioritize low-demand periods, reducing energy costs.
- Each unit is equipped with battery health monitoring systems that alert operators to maintenance needs, ensuring operational readiness during peak times.
Real-Time Task Allocation
- Upon the arrival of a Citation XLS, the tractor is dispatched automatically to retrieve baggage from the ramp area. The dispatch system prioritizes electric vehicles over traditional diesel-powered units to meet sustainability targets.
Performance and Load Management
- Advanced torque control ensures the tractor can handle heavy baggage loads, such as oversized equipment for a medevac mission, without performance degradation.
At a busy business aviation hub, the airport transitions from diesel-powered GPUs to electric units while installing energy-efficient charging stations. This shift results in an annual reduction of 1,200 metric tons of CO₂ emissions, comparable to the yearly emissions of 250 mid-sized cars.
7. Data Integration and Systems Interoperability
Modern ground handling operations rely on seamless data integration and system interoperability to ensure efficiency and accuracy. By connecting systems such as baggage handling systems (BHS), flight information systems (FIS), and resource management systems (RMS) through middleware solutions and standardized data exchange protocols, operators can achieve streamlined workflows and reduce errors.
Real-Time Baggage Handling Coordination
The middleware connects the BHS with the FIS, ensuring real-time synchronization of flight schedules, gate assignments, and baggage routing.
For example; A baggage cart is loaded for a Bombardier Challenger 300 scheduled to depart from Gate 5. The FIS detects a gate change to Gate 12 due to an unforeseen delay in the original departure area. The middleware communicates this change to the BHS. The BHS dynamically adjusts conveyor belt paths, redirecting baggage initially assigned to Gate 5 toward Gate 12. Ground crew receives automated notifications on handheld devices, ensuring timely physical transfer of items from one gate to another, minimizing delays.
Impact
- Reduced instances of baggage misrouting or delays caused by manual communication errors.
- Enhanced passenger satisfaction and reduced claims for mishandled luggage.
Coordinating Ground Crew Deployment
Resource Management Systems (RMS) integrates with the Flight Information Systems (FIS) to monitor real-time flight schedules:
As an example of a Gulfstream G600 scheduled to arrive 15 minutes earlier than planned, the system detects the change and automatically reallocates ground handling teams and equipment to accommodate the new schedule.
Task Prioritization
- Resource Management Systems (RMS) assigns high-priority tasks, such as refueling and GPU setup, to available teams and communicates these tasks to mobile devices used by ramp agents.
- Equipment such as electric GPUs and baggage carts is pre-positioned at the revised gate, ensuring operations can commence immediately upon the aircraft’s arrival.
Real-Time Monitoring and Feedback
- Supervisors can track task progress and equipment availability in real time, adjusting assignments as needed to address delays or unexpected disruptions.
Impact
- Faster turnaround times through precise task coordination and resource allocation.
- Reduced operational bottlenecks, even during peak traffic periods.
Integrated Weather Monitoring Systems
Middleware connects the FIS with weather monitoring systems to provide up-to-the-minute updates on weather conditions. If adverse weather conditions require rerouting or delays, the FIS communicates this information to the RMS, which dynamically adjusts gate assignments and equipment deployment plans. This reduces congestion and ensures passenger safety during peak operational periods.
As a result, middleware integration between the RMS and BHS reduced turnaround times by 20%, allowing the operator to handle 15% more daily movements without additional staffing. Coordinated real-time updates between systems reduced baggage mishandling incidents by 30%, enhancing client satisfaction.
Just Aviation is dedicated to delivering efficient and reliable solutions for the complexities of ground handling. By integrating ground handling technologies and operational expertise, we streamline workflows to meet the demands of modern aviation. Our commitment to precision and professionalism ensures tailored support that enhances efficiency and elevates performance. With Just Aviation, you can count on innovative strategies designed to optimize every aspect of your operations.