Ground Proximity Warning Systems (GPWS) in Business Aviation
15 March 2025
| By Just Aviation TeamIn business aviation, safety remains a top priority. Ground Proximity Warning Systems (GPWS) and the enhanced EGPWS play a vital role in elevating situational awareness and terrain avoidance. These advanced systems provide real-time alerts and predictive terrain monitoring, enabling operators to make well-informed decisions and ensuring smooth, secure operations in all environments.
What is a Ground Proximity Warning System (GPWS) in Aviation ?
A Ground Proximity Warning System (GPWS) is an aircraft safety system designed to alert pilots of imminent terrain collision risks. It uses radio altimeters, GPS, and other sensors to monitor altitude, vertical speed, and aircraft configuration (e.g., landing gear/flap position). If unsafe terrain proximity is detected, the system triggers visual and audible alerts (e.g., “TERRAIN, PULL UP!”) to prompt immediate corrective action.
During a nighttime approach into a high-elevation airport, GPWS detects a rapid descent rate below a safe glide path and issues a “SINK RATE” warning, allowing the crew to adjust descent parameters.
What is Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning System (EGPWS) in Aviation?
Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning System (EGPWS), also known as Terrain Awareness and Warning System (TAWS), builds on GPWS by integrating a global terrain database, GPS positioning, and predictive algorithms. Unlike GPWS, which relies on reactive inputs (e.g., current altitude), EGPWS anticipates terrain conflicts ahead of the aircraft’s flight path.
While navigating through mountainous terrain, EGPWS displays a color-coded terrain map on the navigation screen and warns pilots of a ridge 10 nm ahead, enabling proactive rerouting.
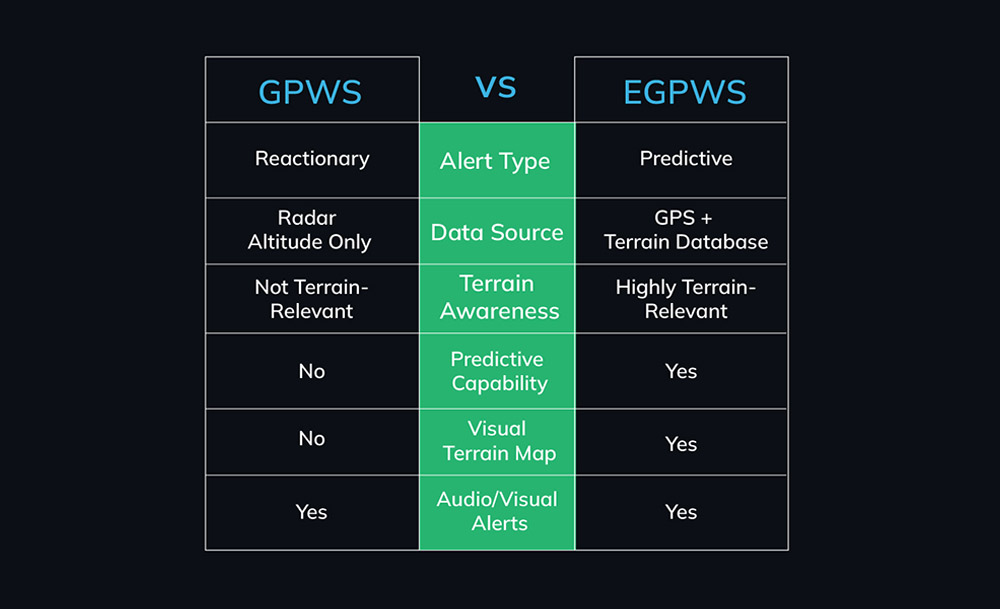
Key Differences Between EGPWS & GPWS in Aviation
| GPWS | EGPWS |
| Relies on radio altimeter and immediate flight parameters. | Adds GPS, terrain databases, and forward-looking capabilities. |
| Reactive alerts (e.g., excessive descent rate). | Predictive alerts (e.g., terrain ahead based on flight path). |
| Limited to “look-down” functionality. | Includes “look-ahead” terrain mapping. |
| No terrain display. | Provides cockpit terrain visualization. |
| Less effective in abrupt terrain (e.g., cliffs). | Mitigates “blind spots” with database-driven awareness. |
Key Features of GPWS and EGPWS
| GPWS | EGPWS |
| Core Modes | |
| Excessive descent rate | Forward-looking terrain avoidance |
| Excessive terrain closure rate | Premature descent alert (e.g., “TOO LOW – TERRAIN”) |
| Altitude loss after takeoff | Runway overshoot/undershoot warnings |
| Unsafe terrain clearance (e.g., gear up) | |
| Alerts | |
| Reactive alerts based on real-time data | Visual and aural alerts for terrain hazards |
| Terrain Display | |
| N/A | Visual map overlay for situational awareness |
| Database | |
| N/A | Customizable updates for obstacles, airports, and terrain |
Benefits of GPWS/EGPWS in Business Aviation
- Enhanced Safety Assurance: Provides crucial protection for terrain awareness in business jet operations.
- Greater Operational Flexibility: Enables safer navigation in low-visibility and mountainous environments.
- Regulatory Compliance: Aligns with ICAO/FAA safety requirements for turbine-powered aircraft.
- Optimized Cost Management: Supports efficient operations by mitigating unforeseen safety risks.
How GPWS/EGPWS Prevents Controlled Flight into Terrain (CFIT)
CFIT occurs when an airworthy aircraft is unintentionally flown into terrain. GPWS/EGPWS mitigates this by:
- Providing Timely Alerts: Early warnings for pilots to ascend or change course.
- Enhancing Situational Awareness: EGPWS displays terrain relative to the flight path.
- Addressing Human Error: Overcomes navigational mistakes in poor visibility or complex terrain.
During a non-precision approach in fog, EGPWS detects the aircraft descending below a safe altitude 3 nm from the runway and issues a “TOO LOW – TERRAIN” alert, prompting a go-around.
Challenges and Limitations
- Database Updates: EGPWS requires regular terrain/obstacle database refreshes.
- False Alerts: Overly sensitive systems may trigger unnecessary warnings (e.g., steep approaches).
- Training Gaps: Pilots must understand alerts and respond appropriately.
- Terrain “Shadow” Zones: GPWS may miss sudden elevation changes without EGPWS’s predictive capability.
GPWS Application for Ground Operations
Engine Run-up
During pre-flight engine run-up procedures on the ground, GPWS can activate if the aircraft’s nose is raised, and its altitude falls below the TCF threshold. This emphasizes the importance of ensuring the GPWS is correctly configured for ground operations.
Taxiing and Maneuvering
GPWS systems in modern business jets might have additional features for taxiing and ground operations. For instance, the system could include a “Runway Awareness and Advisory System” (RAAS), providing aural advisories during taxiing to prevent runway incursions.
Obstacle Clearance
While taxiing on the ground, GPWS can warn pilots if the aircraft gets too close to obstacles, buildings, or terrain. This is particularly relevant when taxiing in congested or unfamiliar airport environments.
Misaligned Takeoff
During takeoff, if the aircraft’s nose is pitched unusually high (indicative of a misaligned takeoff), the GPWS might activate, alerting pilots to correct the takeoff angle to ensure safe ascent.
Approach to Short Runways
When approaching shorter runways, business jet pilots might steepen their descent rate. GPWS will monitor this descent and activate the SR warning if the rate becomes excessive, prompting the crew to adjust their approach profile.
For flight safety business jet operators, integrating GPWS awareness into ground and flight operations is essential. Regular training sessions can simulate scenarios specific to ground operations, ensuring pilots respond effectively to GPWS warnings during various phases of flight and ground activities.
Practical Integration and Oversight
Business flight departments must systematically integrate GPWS/EGPWS (TAWS) into their operations to meet safety and regulatory standards:
Regulatory context
In the U.S., 14 CFR 91.223 and related rules mandate TAWS on most turbine airplanes with six or more passenger seats. Similarly, on-demand charter (Part 135) and commercial (Part 121) operations require Class A or B TAWS depending on aircraft size. European (EASA) and ICAO rules have equivalent CFIT-avoidance requirements. Flight departments should be aware of these mandates and any national variations. For example, Part 135 jets with 10+ seats need the full EGPWS terrain display, while smaller jets (6–9 seats) need at least basic TAWS.
Documentation and Procedures
Official guidance is clear that GPWS/TAWS use must be codified in manuals. The Aircraft Flight Manual (AFM) or Pilot Operating Handbook must include proper TAWS usage instructions and prescribed responses to alerts. Likewise, the Operations Manual or equivalent should address CFIT-avoidance procedures and TAWS policy
This means including bulletins or sections on TAWS alerts, requiring immediate escape maneuvers, and prohibiting disabling the system outside approved exceptions. Dispatchers and coordinators should confirm that the TAWS status is logged in preflight releases and that any maintenance deferrals comply with regulations (often TAWS can’t be deferred if it’s required equipment). If TAWS is inoperative on a flight that requires it, the flight may not be dispatched until it’s repaired.
Maintenance and Updates
The integrity of GPWS/EGPWS relies on current data and system health. Maintenance programs must include the TAWS in the Scheduled/Non-Scheduled maintenance tasks and the Minimum Equipment List (MEL) if applicable. Importantly, the terrain database needs regular updating: FAA guidance specifies that TAWS installations must accept updates, and operators should be informed of and apply them.
Flight departments typically coordinate with avionics maintenance or OEM data providers to install new terrain/obstacle data quarterly or per provider schedule. The system’s coverage area (e.g. “North America” or specific regions) should be identified in the AFM/maintenance documents so dispatchers know which updates are needed for planned trips. For example, if a department plans a flight to the Alps but the TAWS database covers only North America, they must update the data beforehand. Day-to-day, preflight checks include verifying TAWS power-up tests and ensuring any required sensors (like radio altimeters for Class A) are functional.
Technical Requirements For A Ground Proximity Warning System (GPWS)
Implementing a Ground Proximity Warning System (GPWS) involves various technical requirements to ensure the system’s effectiveness in enhancing safety during flight and ground operations. Below are the key technical requirements for a GPWS:
Radar Altimeters
GPWS relies on radar altimeters to accurately measure the aircraft’s height above the terrain. Multiple radar altimeters enhance accuracy and redundancy. These instruments continuously provide altitude data, enabling the system to calculate and compare the aircraft’s position relative to the ground.
Terrain Database
A comprehensive and up-to-date terrain database is essential. It contains elevation data and terrain features, helping the GPWS to calculate the minimum safe altitude for different phases of flight. This database is regularly updated to ensure accuracy.
GPS Integration
Global Positioning System (GPS) data provides accurate and real-time information about the aircraft’s position, enhancing the precision of GPWS warnings. Integration with GPS systems allows the GPWS to account for the aircraft’s lateral position as well.
Flight Control Interface
GPWS needs a seamless interface with the flight control system. This ensures that warnings are relayed to the flight crew through appropriate displays, indicators, and auditory alerts.
Altitude Callouts
The system should provide altitude callouts during various phases of flight to assist pilots in maintaining proper altitude profiles during descent, approach, and landing. These callouts serve as reminders for altitude awareness.
Warning Generation Algorithm
GPWS employs complex algorithms to calculate and predict the aircraft’s trajectory relative to the terrain. It compares actual flight parameters with predefined safety margins to determine if a warning is necessary.
Auditory and Visual Alerts
GPWS issues both auditory and visual alerts to pilots. Auditory alerts are typically prioritized due to their immediate attention-grabbing nature. Visual alerts on cockpit displays provide additional cues.
Integration with Enhanced Vision Systems
Integration with enhanced vision systems, such as Synthetic Vision Systems (SVS) and Enhanced Vision Systems (EVS), enhances situational awareness by providing pilots with a virtual view of the terrain in low visibility conditions.
Customizable Warnings
Operators should have the ability to customize the warning messages and levels according to their operational needs. This ensures that the system aligns with the operator’s standard operating procedures.
Integration with Cockpit Instruments
GPWS warnings should be integrated with other cockpit instruments, such as the primary flight display (PFD) and navigation display (ND), for immediate pilot response.
Data Recording and Analysis
GPWS systems often come with data recording capabilities. This allows operators to review flight data after an event and analyze how warnings were triggered, contributing to safety enhancements.
A well-designed GPWS integrates multiple technical components, including radar altimeters, terrain databases, GPS, warning algorithms, and intuitive interfaces, to provide timely and accurate alerts to flight crews. By meeting these technical requirements a GPWS contributes significantly to aviation safety by preventing controlled flight into terrain incidents.
GPWS Installation Checklist
GPWS installation checklist involves a comprehensive checklist to ensure that the system is integrated correctly and functions as intended. Here’s a checklist outlining key steps for GPWS installation.
Pre-Installation Preparation
- Review Specifications: Understand the technical requirements and specifications of the GPWS system to ensure compatibility with the aircraft type and operational needs.
- Select Suitable Location: Determine the optimal location for installing GPWS components in the aircraft, considering factors such as accessibility, visibility for crew, and interference with other avionics.
- Obtain Manuals: Obtain installation manuals and documentation provided by the GPWS manufacturer. These resources provide step-by-step guidance for installation procedures.
Physical Installation
- Mounting and Hardware: Securely mount GPWS components, including radar altimeters, control units, displays, and any associated hardware, adhering to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Wiring and Connections: Carefully route and connect wiring between components, ensuring proper shielding, separation from power lines, and adherence to electrical guidelines.
- Antenna Installation: If applicable, install GPWS antennas according to specifications, considering factors such as signal propagation and interference.
Integration and Testing
- System Integration: Integrate GPWS with existing avionics systems, including GPS, flight control interfaces, and other warning systems, following manufacturer guidelines.
- Functional Tests: Conduct functional tests to verify that all components are properly connected and operational. Test each GPWS mode (TCF, EDR, SR, etc.) to ensure accurate alerts and callouts.
- Data Accuracy Verification: Verify that GPS data and terrain databases are accurately integrated with the GPWS system, ensuring precise altitude calculations and warnings.
Interface and Displays
- Cockpit Displays: Install GPWS alerts and displays in visible and accessible locations within the cockpit, such as on the primary flight display (PFD) and navigation display (ND).
- Auditory Alerts: Integrate auditory alerts into the cockpit audio system, ensuring clear audibility and distinctiveness from other warning sounds.
Calibration and Configuration
- Calibration: Calibrate radar altimeters and other sensing components according to manufacturer guidelines to ensure accurate altitude measurements.
- Configuration: Configure GPWS modes and settings to align with the aircraft’s operational profile, including altitude thresholds, warning levels, and callout preferences.
FAQs
1. What are GPWS/EGPWS (TAWS)?
GPWS (Ground Proximity Warning System) and its enhanced form (often called EGPWS or TAWS) are onboard alert systems that warn flight crews of imminent terrain or obstacle conflicts. These systems help prevent Controlled Flight Into Terrain (CFIT) by providing timely aural and visual alerts. The “enhanced” TAWS adds a digital terrain database and forward-looking capability, giving crews earlier warnings and more time to react than the older basic GPWS.
2. Which business aircraft require EGPWS/TAWS?
U.S. regulations require all turbine-powered airplanes with six or more passenger seats (excluding pilots) to have an approved TAWS onboard. This covers most mid-size and larger business jets. For Part 135 charter operations, the rule is stricter: jets with 10 or more seats must carry a full Class A TAWS (with terrain display) and those with 6–9 seats need at least Class B TAWS. (These aircraft cannot legally operate in commercial or charter service without the required TAWS equipment.)
3. What documentation and training are required?
The rules mandate that aircraft manuals include TAWS procedures. For example, 14 CFR 91.223(c) requires the Airplane Flight Manual (AFM) to contain proper TAWS use and crew-response procedures. Operators’ manuals must also cover CFIT-avoidance policies and when/how TAWS is used in standard procedures. Regulators expect pilot training to address TAWS alerts. FAA guidance explicitly calls for initial and recurrent simulator training of the published ground-proximity escape maneuver (used when a TAWS warning occurs) at least every 24 months.
4. Who maintains and updates the terrain databases?
The flight department must ensure TAWS terrain/obstacle data is kept current. FAA guidance says the equipment installer or manufacturer should notify the operator about data updates, and operators should install updates after reviewing them. Operators should note the database’s geographic coverage in the AFM or maintenance documents (e.g. North America, Europe) and verify it matches planned routes.
5. Are there any exceptions or special cases?
Very few. For instance, 14 CFR 91.223(d) explicitly exempts certain local missions (like parachute drops within 50 NM of base) from the TAWS requirement. Outside those narrowly defined operations, any covered turbine aircraft must have TAWS enabled. In other words, flight ops should treat TAWS as mandatory equipment and generally do not disable it during revenue operations.
6. How should a flight department manage TAWS in operations?
Think of TAWS like any required safety system: include it in checklists, maintenance logs, and flight releases. For example, before each flight the dispatcher or operator should verify the TAWS is serviceable and properly configured. Company SOPs and the Operations Manual should document how TAWS alerts are handled (in line with regulatory guidance on CFIT avoidance). This means training pilots on the escape maneuver and ensuring dispatchers plan routes with required terrain data loaded. By incorporating TAWS compliance into manuals, training, and briefings (as required by regulation) flight operators can ensure the system truly enhances safety and meets all official standards.
7. Does EGPWS function reliably in remote or poorly mapped regions?
EGPWS depends on GPS accuracy and database completeness. In remote areas (e.g., Arctic regions or mountainous terrain), GPS signal reliability may degrade, and terrain mapping might lack granularity. Operators should combine EGPWS with:
- Pre-flight analysis of sectional charts.
- Redundant altimetry checks.
- Conservative altitude margins (e.g., +1,000 ft over uncharted peaks). While EGPWS reduces risks, it cannot compensate for incomplete regional data.
In the dynamic world of business aviation, GPWS and EGPWS are indispensable tools for enhancing safety and preventing CFIT incidents. At Just Aviation, we understand the critical role these systems play in ensuring seamless flight operations. By combining advanced technology with expert flight support, we empower operators to navigate safely, comply with regulations, and achieve operational excellence. Trust Just Aviation to elevate your safety standards and optimize operational efficiency in flight operations.