Our Blog
Airport Ground Handling Services Importance and The Differences in Ground Operation for Private Jets & Commercial Aircraft
22 July 2024
| By Just Aviation TeamWhat is Ground Handling?
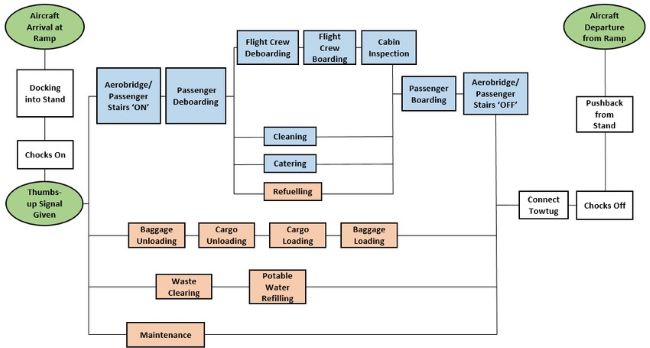
Ground handling encompasses a range of essential services provided to an aircraft while it is on the ground. These services include both customer service functions (e.g., ticketing, check-in, baggage sorting, and passenger boarding) and ramp services (e.g., marshaling, baggage loading, refueling, and providing ground power). Ground handling is crucial for ensuring that aircraft are prepared for their next flight and that passengers transition smoothly between the terminal and the aircraft.
Why is Ground Handling Important?
Ground handling is essential for several reasons:
- Safety and Comfort: Manages baggage, facilitates boarding, and prepares the aircraft cabin to ensure passenger comfort and safety.
- Efficiency: Minimizes turnaround time, which helps maintain flight schedules and reduce costs.
- Passenger Experience: Enhances overall satisfaction through efficient service and timely departures.
- Aircraft Maintenance: Provides necessary maintenance and servicing between flights to keep the aircraft in optimal condition.
Difference between FBO, Ground Handling And Supervisory Agent
Within the aviation industry, there are various service providers that provide support to aircraft:
1. Fixed Base Operator (FBO)
FBO services include:
- Refueling: Includes quality control and safety measures.
- Hangar Rental: Secure storage with climate control.
- Aircraft Preservation: Cleaning, detailing, and protection.
- Pre-Flight Preparation: Flight planning, customs handling, and passenger services.
2. Ground Handling
Ground Handling encompasses all operations performed on an aircraft while it is on the ground, including passenger, cargo, ramp services, and maintenance. Ground Handlers Components are:
- Passenger Handling: Check-in, boarding, and baggage management.
- Cargo Handling: Loading, unloading, and security.
- Ramp Handling: Aircraft marshaling and ground power supply.
- Catering: Food and beverage services, ensuring hygiene.
- Cleaning and Maintenance: Routine cleaning and minor repairs.
3. Supervisory Agent
Supervisory Agent is an individual or entity responsible for coordinating and managing ground handling services, including flight planning and regulatory compliance. Supervisory Agent responsibilities are:
- Flight Planning and Coordination: Scheduling and integrating services.
- Air Traffic Control Liaison: Managing communications and tracking.
- Ground Operations Management: Overseeing service execution and resolving issues.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring adherence to regulations and documentation.
What are the Disparities in the Ground Handling Procedures Between Private Jets and Commercial Airlines?
Private jets and airlines differ in their airport ground handling requirements due to differences in their operations.
Private Jets: These operations require high levels of customization. Services include expedited check-in, private security checks, and personalized flight planning. The ground handling process is streamlined but tailored to individual client needs, often involving minimal staff and direct services to enhance the passenger experience and meet specific requests.
Commercial Airlines: Handling procedures are more complex due to the higher volume of passengers and cargo. Services are standardized to manage large-scale operations efficiently. This involves extensive coordination among multiple teams and adherence to strict regulatory requirements, ensuring that all aspects of ground handling, from check-in to baggage management, are executed seamlessly and on a larger scale.
The table below will further explain the differences in ground handling requirements between private jets and airlines:
| Ground Handling Aspect | Private Jets | Airlines |
| Passenger and Crew Needs | Emphasizes high-priority, bespoke services including rapid check-in (e.g., using VIP terminals), private security screening (compliant with TSA’s VIP screening protocols), and personalized in-flight amenities (adhering to FAA’s cabin safety regulations). | Requires standardized procedures to handle large passenger volumes and crew efficiently. Services align with ICAO’s standard procedures and IATA’s guidelines for passenger management. |
| Flight Planning | Involves complex, adaptive flight planning with real-time adjustments. Flight plans often include bespoke routing and modifications based on client requests, using tools for flight planning services and compliance with FAA Part 91 regulations for private operations. | Generally follows standardized flight planning with set schedules. Flight plans adhere to ICAO standards and FAA Part 121 regulations for commercial operations, ensuring consistency and operational efficiency. |
| Airport Size | Operates from smaller, less congested airports or dedicated private terminals, which allows for streamlined operations. Relevant regulations may include the FAA’s General Aviation Facilities and Services guidelines and specific airport procedures for smaller airports. | Utilizes larger, high-traffic airports with complex infrastructure. Compliance with ICAO’s Airport Services Manual and IATA’s Ground Operations Manual is critical for managing extensive passenger and cargo volumes. |
| Service Expectations | Demands high levels of personalization including customized ground services (e.g., tailored VIP lounges), exclusive amenities, and specialized catering services (following HACCP guidelines for food safety in aviation). | Services are standardized to ensure efficiency, with adherence to ICAO’s Ground Handling Manual and IATA’s Airport Handling Manual for uniform procedures in check-in, boarding, and ground support. |
| Coordination & Management | Features simplified coordination with fewer stakeholders, such as directly liaising with Fixed Base Operators (FBOs) and utilizing less formal management frameworks. Compliance with FAA regulations and industry best practices for private aviation ensures streamlined operations. | Involves complex coordination among multiple service providers, integrating aspects like ramp handling, cargo management, and airside services. Adheres to comprehensive standards outlined in the ICAO’s Document 9137 and the IATA’s Handling Manual for detailed operational protocols. |
Key Ground Handling Operations
Efficient ground handling operations are crucial for ensuring the safe and timely arrival and departure of aircraft. Some of the most commonly used ground handling operations include aircraft marshaling, baggage and cargo handling, ramp handling, aircraft refueling, cleaning and maintenance, catering, passenger and crew transportation, and de-icing.
Hangar Parking Operations
The size and characteristics of hangars for business jets may vary depending on the type and size of aircraft. Hangars are specially designed for the protection and safe parking of aircraft. For example, a hangar’s ventilation system is designed to help cool aircraft engines. Hangars also contain special equipment and tools for the maintenance of aircraft. Major Services are:
- Minimum Runway Strip Requirement: Hangar parking services for business jets must meet the aircraft’s minimum runway strip requirement. This requirement differs depending on the wingspan of the aircraft and the air traffic of the landing airport.
- Aircraft Stand Positioning: It is the process of determining the necessary placement positions within the hangar for safe and efficient parking of aircraft. This process differs based on factors such as aircraft type, size and wingspan.
- Engine Run-up Area: It is the open area required for engine testing during the maintenance of business jets. Engine testing is done to ensure that all the systems required for safe flight are working properly.
Maintenance Services
Maintenance services for business jets include the elimination of all mechanical, electronic and structural problems of the aircraft. Maintenance services are extremely important to ensure planes fly safely. For example, maintenance services include engine maintenance, testing and repair, structural maintenance and checking of electronic systems. Maintenance services are performed according to standards set by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA).
- Line Maintenance: It is the regular maintenance service of business jets. This service ensures that the aircraft is ready for use every time. Line maintenance services include oil change, filter change, tire change.
- Base Maintenance: It is the basic maintenance service of airplanes every 3-4 years. This service includes more thorough inspection and maintenance of the aircraft. Some basic maintenance services include engine maintenance, avionic systems maintenance, paint renewal.
- Unscheduled Maintenance: Emergency maintenance service for business jets. This service covers maintenance services that need to be intervened in the event of a sudden malfunction in the aircraft.
- Scheduled Maintenance: It is the maintenance service that needs to be done on aircraft at certain periods. This service is provided on predetermined dates and times. Scheduled maintenance services include calibration services, annual maintenance, regular tests and inspections.
Deicing and Anti-icing Operations
Deicing and anti-icing are vital tools for coping with operations in bloodless weather conditions to ensure the safety of the aircraft. Deicing is the way of putting off snow, ice, and frost from the aircraft surfaces, simply as anti-icing is the technique of stopping the formation of ice on the aircraft surfaces at some stage inside the pre-flight practice system.
- De-icing fluid is sprayed onto the aircraft using an excessive-stress hose, generally containing glycol or propylene glycol, which lowers the freezing component of water and breaks down the ice. The fluid is heated to a specific temperature, relying on the ambient situations and the kind of plane, to ensure it is powerful enough to melt the ice.
- The de-icing system is finished on all vital surfaces of the aircraft, which includes the wings, tail, and fuselage. After de-icing, the aircraft must be cleared of any final fluid to avoid refreezing and potential damage to the engines and sensors.
- Anti-icing fluid commonly incorporates a higher concentration of glycol or propylene glycol than de-icing fluid, and it’s far more designed to adhere to the aircraft’s surfaces for an extended duration. The fluid is also heated to a particular temperature to ensure it stays powerful in cold conditions.
- Anti-icing is applied on all critical surfaces of the aircraft, which consist of the wings, tail, and fuselage. Anti-icing is applied to all vital surfaces of the plane, consisting of the wings, tail, and fuselage. The anti-icing fluid must be reapplied if the aircraft experiences a significant delay before takeoff to ensure continued protection.
Baggage and Cargo Handling Operations
Bags and cargo dealing consists of a selection of technical operations, inclusive of the use of specialized systems along with cargo handlers, forklifts, and vendors to load and sell off aircraft. The shipment has to additionally be nicely secured to prevent slipping at some point in flight, which could have an effect on the steadiness of the plane. Operations used in baggage and cargo handling include:
- Weight and balance calculations: Ensuring that the weight and balance of the aircraft are within safe limits.
- Loading and unloading procedures: Following strict procedures to prevent damage to aircraft or cargo.
- Handling hazardous materials: Complying with regulations and safety procedures when handling hazardous materials such as chemicals or batteries.
- Compliance with security regulations: Following protocols to prevent aircraft intrusions and ensure the safety of baggage and cargo.
Refueling Services
Business jet operators need refueling services to keep their planes running. Refueling can take from 10 minutes to an hour, depending on the size of the plane and the amount of gas required. Business jet operators often need fast turnarounds that require fast and efficient refueling services. Some of the procedures related to aircraft refueling are:
- Sequencing: The process of directing the aircraft to the correct park position using signals.
- Fuel Quality Control: Visual inspection of the fuel for contaminants and water before refueling begins.
- Bonding and Grounding: To ensure the aircraft and fuel truck are grounded and electrically bonded to prevent static electricity build-up and sparks.
- Refueling Process: The fuel truck operator connects the fuel hose to the aircraft and the fuel is pumped into the tanks at the specified rate and pressure.
- Fuel Quantity Control: The delivered fuel quantity is checked against the quantity requested to ensure accuracy.
- Fuel Tank Ventilation: The venting system is checked for blockages or leaks to ensure fuel tanks are properly ventilated during refueling.
- Fuel Tank Cap Sealing: After refueling, the fuel tank caps are tightly sealed to prevent fuel leaks during flight.
Catering Services
Catering for business jets is designed to meet the special needs of passengers during flight. For example, food and beverages used in private jets must be stored and served in accordance with hygiene conditions. Catering services also include the cleaning of materials and equipment used in the aircraft in accordance with hygienic conditions.
Crew Transportation
Crews of business jets also need special transportation services. This service includes transporting the crew to the aircraft, providing accommodation and meals. In addition, all the services that the crew may need before and after the flight are also provided.
Passenger Transportation
Passenger transportation services for business jets encompass a range of services, including airport and hotel transfers before and after the flight. These services are designed to make the travels of private jet owners and passengers more comfortable and hassle-free.
Just Aviation recognizes the importance of efficient ground handling services for a seamless travel experience. With our commitment to excellence and attention to detail, we strive to provide the highest quality of ground handling services to our clients. Trust Just Aviation to provide comprehensive ground handling solutions tailored to your aviation needs.